Section outline
-
Preserving and enhancing the microbiomes of urban forests can maximize their benefits for human health.
· Biodiverse green space design
Incorporating native plants and minimizing soil sealing can protect microbial habitats. Green roofs, urban parks, and reforestation projects provide opportunities to restore microbial diversity (9).
· Pollution mitigation strategies
Reducing pollutants through waste management and bioremediation supports the detoxification functions of forest microbiomes. This creates a safer environment for both urban ecosystems and their human populations (9,12).
· Community engagement and citizen science
Educating communities about the importance of urban forest microbiomes fosters public support for conservation. Citizen science projects that monitor soil and tree health can directly involve urban populations in preserving forest microbiomes (7).
· Integration in urban planning
Urban planning that prioritizes connectivity between forest patches, reduces fragmentation, and incorporates green corridors can enhance microbial exchange and diversity across urban forests (7,12).
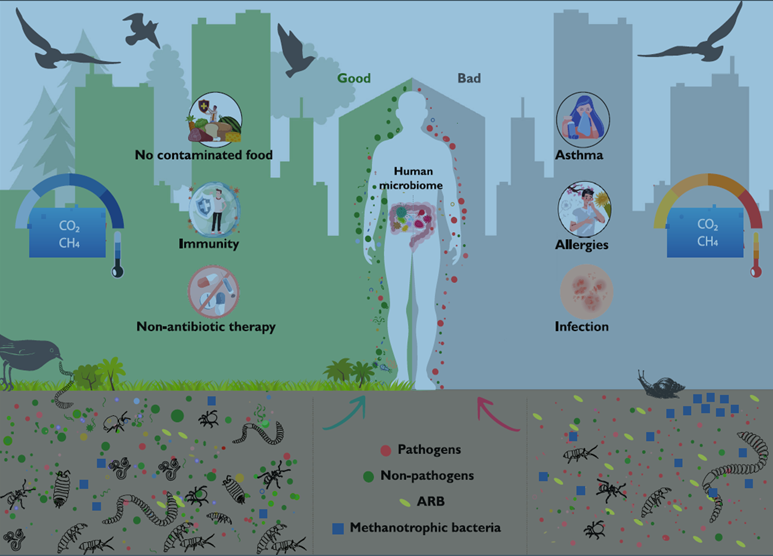
Image 3. Microbial diversity supports urban health by enhancing soil health, suppressing pathogens, reducing pollutants, and boosting human immunity and microbiome regulation (12).